Parents always hope for their children to be born healthy and normal. So, if, unfortunately, a child experiences delayed intellectual development, what should you do? Through the following article, we will help you understand the causes, signs, and ways to address this condition in children.
-
What is delayed intellectual development in children?
Delayed intellectual development refers to deficiencies in the child’s brain development process. When certain brain functions are limited, the child’s intelligence quotient (IQ) falls below average. Additionally, abilities such as communication, behavior, and learning tend to be slower compared to other children.
Delayed intellectual development usually occurs in children under 18 years old and is categorized into four levels:
Mild:
Statistics show that about 80% of children with delayed intellectual development are at a mild level. Their IQ ranges between 50 – 75, allowing them to attend elementary school. Although it may take longer to learn skills such as communication, reading, and writing, with proper support and education, these children can still excel academically. Therefore, as they grow older, they can become self-sufficient.
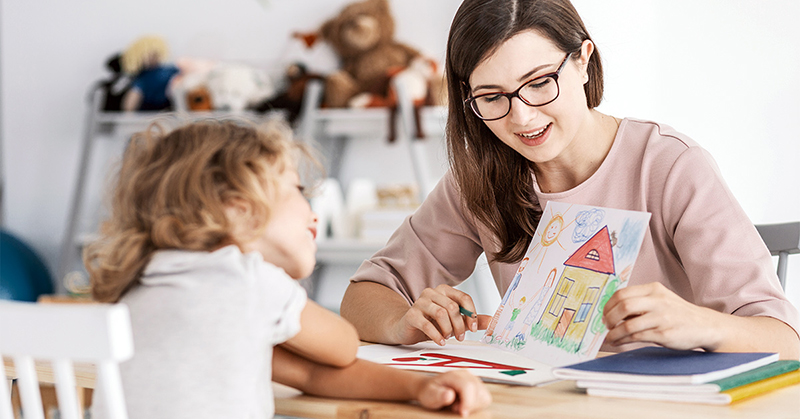

If provided with proper support and education, children with mild delayed intellectual development can still excel academically.
Moderate:
At the moderate level of delayed development, children typically have an IQ ranging from 35 – 55. Consequently, they can perform basic daily activities such as bathing and eating under parental guidance. Moreover, they can learn to read, write, and count, albeit at a slower pace. Thus, as they grow, these children require supervision and care from others.
Severe:
Only about 3 – 5% of children experience severe delayed development. At this level, their IQ ranges from 20 – 40, enabling them to learn communication skills and self-care. However, as they mature, these children need to live in supervised communal settings.
Profound:
Children with profound delayed development are relatively rare, accounting for only 1 – 2%. Due to damage to the nervous system, their IQ remains below 20 – 25. Consequently, they require constant guidance and assistance from parents to learn basic communication skills and self-care.
- Causes of delayed intellectual development in children
If, unfortunately, your child shows slower cognitive development compared to peers, instead of feeling embarrassed, you should accompany them to identify the causes and devise effective remedies.
Here are some causes of delayed intellectual development in children:
Genetics:
If parents have neurological abnormalities, the risk of their child experiencing delayed intellectual development is significantly higher. Additionally, metabolic disorders such as Phenylketonuria (PKU) in parents can also contribute to this condition.
Issues during pregnancy:
Maternal lifestyle habits directly influence fetal development. Therefore, experiencing the following issues increases the risk of delayed intellectual development in children:
- Regular exposure to cigarette smoke, alcohol, drugs, especially during the first three months of pregnancy.
- Contracting diseases such as rubella, parasitic infections, disorders of the pituitary gland, or viral infections.
- High blood pressure leading to disrupted blood flow to the fetus, affecting brain development.
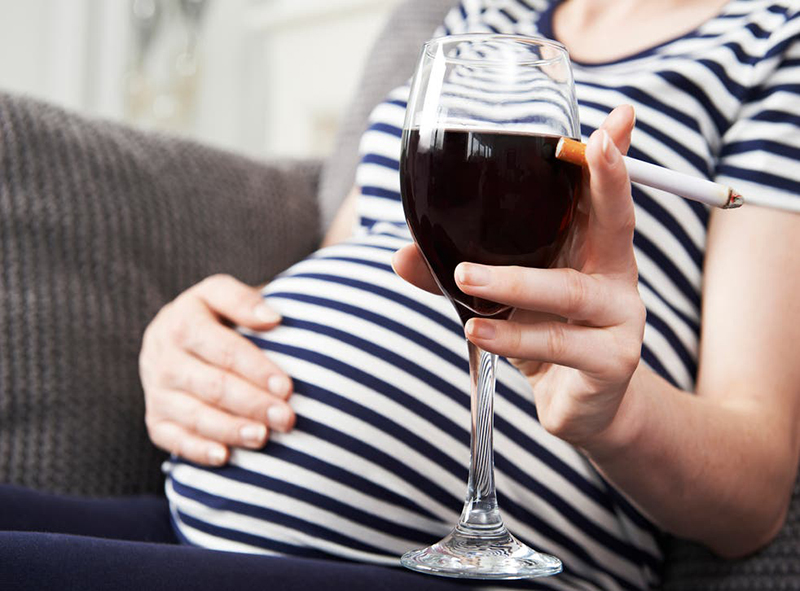

Fetal development can be affected if mothers are regularly exposed to cigarette smoke, alcohol, or drugs, especially during the first three months of pregnancy.
Illnesses and injuries:
Since a child’s immune system is not fully developed at birth, it cannot effectively combat external factors. Therefore, without complete vaccination against diseases such as measles, mumps, children are susceptible to complications affecting the brain. Particularly, conditions like encephalitis, meningitis, can cause damage leading to delayed intellectual development. Additionally, everyday accidents or falls from heights can also contribute to this condition.
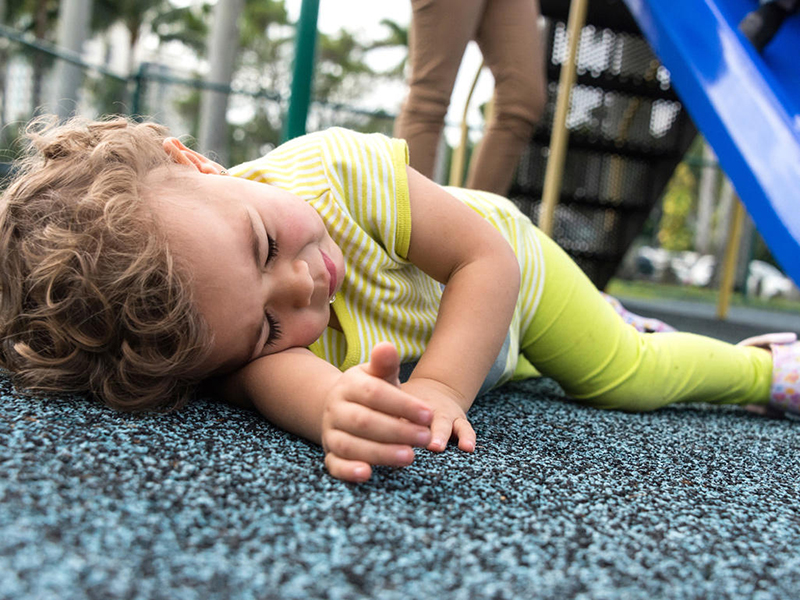

Living environment:
Living in a polluted environment with various harmful substances can hinder a child’s development. Moreover, a child’s mental well-being is compromised in violent or unloving environments. Furthermore, inadequate nutrition during pregnancy and after birth can result in weakness and delayed brain development in children.
- Signs of recognizing delayed intellectual development in children
Here are some signs to help parents recognize if their child is experiencing delayed intellectual development:
- Sitting, walking later than other children.
- Unclear speech.
- Poor memory, difficulty remembering simple information such as names or recent events.
- Learning skills like eating, dressing slowly, requiring assistance from others.
- Difficulty concentrating, understanding, or thinking logically.
- Can delayed intellectual development in children be treated?
Whether delayed intellectual development in children can be treated is always a concern for many parents when facing this situation. Instead of worrying, parents should intervene promptly to help improve their child’s cognitive function.
Nutrition:
Nutrition plays a crucial role in a child’s development. Therefore, parents should provide adequate nutrition, especially foods rich in Omega-3 fatty acids such as salmon, tuna, as these foods can improve vision, sleep, and brain development.
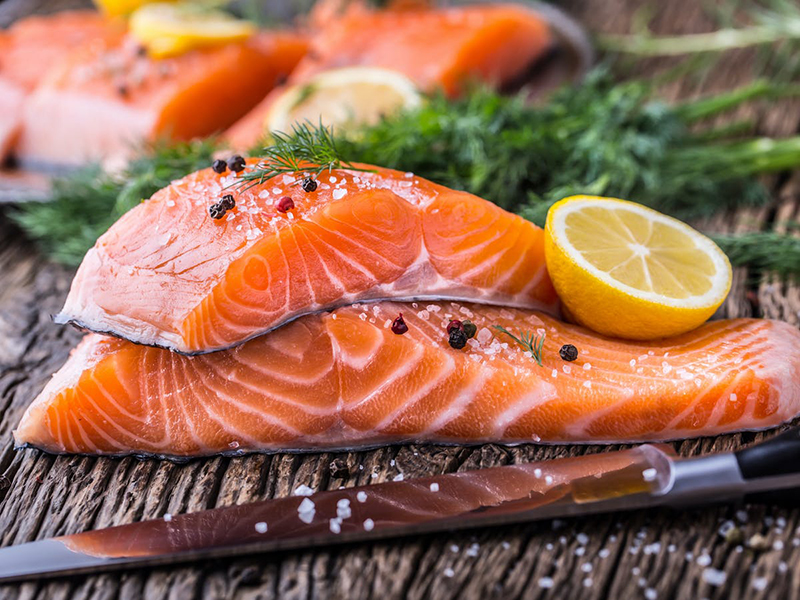

Additionally, parents should supplement their child’s diet with foods rich in vitamins and minerals for comprehensive development.
Education:
The learning process for children with delayed intellectual development is challenging. Therefore, parents should strive to be patient and supportive in helping their child overcome obstacles. Parents should spend quality time guiding and teaching their child. Depending on the level of delayed development, parents can devise a suitable learning plan tailored to their child’s cognitive abilities and behavior.
Psychological therapy:
Children with delayed intellectual development often experience fear or anxiety without clear causes. Therefore, parents should seek counseling for their child when noticing abnormal psychological symptoms. After assessment, a psychologist can devise a treatment plan for the child, which may involve close collaboration with teachers and parents to monitor the child’s behavior.
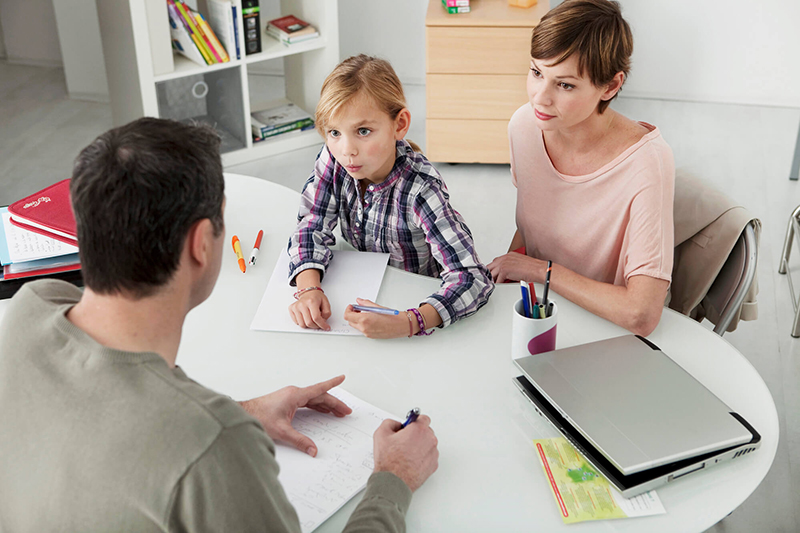

After assessment, a psychologist can devise a treatment plan for the child, which may involve close collaboration with teachers and parents to monitor the child’s behavior.
By reading this article, we hope you have gained insights into the causes, signs, and remedies for delayed intellectual development in children. When detecting abnormal psychological and behavioral symptoms in children, parents should seek counseling to intervene effectively.